Secure Internal Communication: Common Risks and Effective Solutions
Ensuring secure internal communication protects sensitive data, ensures regulatory compliance, and maintains operational integrity, fostering trust and preventing financial and reputational damage.

Secure internal communication is critically important for protecting sensitive company data from unauthorized access — including financial information, strategic plans, and employee details. Not only can it prevent financial and reputational damage, it can also ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, thereby avoiding hefty penalties and fines.
Effective security measures also guard against cyber threats, maintain operational integrity, support business continuity, and enhance corporate governance. By mitigating communication risks, organizations can safeguard their internal operations and maintain stakeholder trust. Understanding these risks helps in implementing robust security practices.
Why your company needs secure internal communication
Securing internal communication, especially within enterprise organizations, is highly critical. Primarily, it safeguards sensitive information such as financial data, strategic plans, intellectual property, and personal employee details from unauthorized access, which could lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX is another critical factor, as failure to secure communications can result in hefty legal penalties. Furthermore, it helps prevent cyber threats such as phishing, social engineering, malware, and ransomware, which can disrupt business operations and cause financial losses.
Ensuring secure communication also maintains operational integrity, supports business continuity, and fosters trust among employees, partners, and customers. Protection against insider threats is crucial, as it helps prevent internal fraud and data leakage. Additionally, secure communication enhances corporate governance by ensuring accountability and traceability, which are essential for effective decision-making and compliance.
Maintaining a positive public image and client confidence is another vital aspect, as security breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation.
Finally, by avoiding financial losses associated with security incidents and improving operational efficiency, securing internal communications results in significant cost savings. According to IBM, the global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 4.45 million.

In light of these reasons, understanding the common safety risks for internal communication becomes imperative for enterprise organizations.
Common safety risks that threaten secure internal communication
1. Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals send deceptive emails or messages to employees, tricking them into revealing sensitive information or installing malicious software.
Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information through psychological manipulation rather than technical hacking methods.
2. Insider Threats
Malicious Insiders: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive information may intentionally misuse their access for personal gain or to harm the organization.
Accidental Data Leakage: Employees may unintentionally share sensitive information through insecure channels or by mishandling data.
3. Malware and Ransomware
Malware Infections: Malicious software can be introduced through email attachments or compromised communication channels, leading to data breaches or system damage.
Ransomware: Attackers encrypt the organization’s data and demand a ransom for its release, disrupting business operations and causing financial losses.
4. Unsecured Communication Channels
Unencrypted Emails: Sending sensitive information through unencrypted email can be intercepted by unauthorized parties.
Insecure Messaging Apps: Using unsecured messaging applications for internal communication can expose sensitive data to interception.
5. Weak Access Controls
Inadequate Authentication: Weak or improperly managed authentication processes can allow unauthorized access to communication channels.
Insufficient Authorization: Failing to properly restrict user permissions can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information.
6. Lack of Security Awareness
Employee Negligence: Employees who are unaware of security protocols may inadvertently compromise internal communications by falling for scams or mishandling information.
Poor Training: Insufficient training on security best practices can leave employees unprepared to identify and respond to threats.
7. Data Interception
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers intercept and potentially alter communication between two parties without their knowledge.
Eavesdropping: Unauthorized individuals may listen in on voice or video communications, capturing sensitive information.
8. Vulnerabilities in Communication Software
Software Exploits: Security vulnerabilities in communication tools or platforms can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or disrupt communications.
Outdated Software: Failure to regularly update communication software can leave systems vulnerable to known exploits.
9. Data Loss or Theft
Physical Theft: Theft of devices such as laptops or smartphones that contain sensitive communication data.
Backup Compromises: Insecure backup procedures can result in unauthorized access to archived communications.
10. Network Security Issues
Insecure Wi-Fi Networks: Using unsecured or poorly protected Wi-Fi networks for internal communication can expose data to interception.
Network Intrusions: Attackers who gain access to the organization’s network can intercept and manipulate internal communications.
How to secure internal communication to prevent leaks
Organizations can take several measures to secure their internal communication and prevent leaks. These measures encompass a range of technological, procedural, and educational strategies designed to protect sensitive information and maintain the integrity of communication channels.
By implementing these measures, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their internal communications, reducing the risk of leaks and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access.
1. Encryption
End-to-End Encryption: Implement end-to-end encryption for all internal communications to ensure that only authorized parties can read the messages.
Secure Email Encryption: Use email encryption tools to protect sensitive information transmitted via email.
2. Strong Access Controls
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require multi-factor authentication for accessing internal communication platforms to add an extra layer of security.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement role-based access controls to ensure that employees have access only to the information necessary for their roles.
3. Secure Communication Platforms
Approved Tools: Use secure, enterprise-grade communication tools that offer robust security features such as encryption, access controls, and regular security updates.
Regular Updates: Ensure that all communication software and tools are regularly updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
 The Staffbase platform, including its employee app and employee intranet, meet stringent ISO 27001 requirements.
The Staffbase platform, including its employee app and employee intranet, meet stringent ISO 27001 requirements.
4. Employee Training and Awareness
Security Training: Provide regular training sessions on security best practices, phishing awareness, and how to handle sensitive information.
Clear Policies: Establish and communicate clear policies regarding the use of communication tools, handling of sensitive information, and reporting of suspicious activities.
5. Monitoring and Auditing
Activity Monitoring: Monitor communication channels for suspicious activity and unauthorized access attempts. Security AI can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to detect and respond to cyber threats.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in communication systems.
6. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools
DLP Solutions: Implement data loss prevention tools that can detect and prevent the unauthorized sharing of sensitive information.
Content Filtering: Use content filtering to scan communications for sensitive data and block unauthorized transmissions.
7. Network Security
Secure Networks: Ensure that all internal communications are conducted over secure, encrypted networks. Avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive communications.
Network Segmentation: Segment the network to limit access to sensitive areas and reduce the impact of potential breaches.
8. Incident Response Plan
Preparedness: Develop and maintain an incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach or data leak.
Regular Drills: Conduct regular drills to ensure that employees are familiar with the incident response plan and can act quickly and effectively.
9. Physical Security
Device Security: Ensure that all devices used for internal communication are secured with strong passwords, encryption, and biometric authentication where possible.
Secure Workspaces: Maintain secure physical workspaces to prevent unauthorized access to devices and sensitive information.
10. Vendor and Third-Party Management
Secure Integrations: Ensure that any third-party services or tools integrated with internal communication systems meet stringent security standards.
Regular Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments of third-party vendors to ensure they comply with the organization’s security requirements.
Best practices for protecting sensitive data
To protect sensitive company data effectively, organizations should adopt a comprehensive approach encompassing a variety of best practices. By implementing these best practices, organizations can create a robust security posture that protects sensitive company data from both internal and external threats.
Here are some key strategies:
1. Data Encryption
End-to-End Encryption: Implement end-to-end encryption for all data in transit and at rest to ensure it remains confidential and secure.
Email Encryption: Use encrypted email services to protect sensitive information shared via email.
2. Access Control
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require MFA for accessing sensitive data and systems to add an additional layer of security.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Implement RBAC to ensure employees only have access to the data necessary for their roles.
3. Regular Security Training
Employee Education: Conduct regular training sessions on data security best practices, phishing awareness, and proper data handling procedures.
Clear Policies: Establish and enforce clear data security policies and protocols.
4. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP Tools: Use DLP tools to monitor, detect, and prevent unauthorized data transfers or leaks.
Content Filtering: Implement content filtering to scan outgoing communications for sensitive information.
5. Secure Communication Channels
Approved Platforms: Use secure communication platforms with robust security features, including encryption and access controls.
Network Security: Ensure all internal communications occur over secure, encrypted networks, and avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive discussions.
6. Regular Audits and Monitoring
Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in the system.
Continuous Monitoring: Implement continuous monitoring of networks and systems to detect and respond to suspicious activities promptly.
7. Incident Response Planning
Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a comprehensive incident response plan to address data breaches and other security incidents.
Regular Drills: Conduct regular drills to ensure employees are familiar with the incident response procedures.
8. Strong Password Policies
Complex Passwords: Enforce the use of strong, complex passwords that are regularly updated.
Password Management Tools: Provide employees with password management tools to securely store and manage their passwords. 1Password is a great example of such tools.
9. Software and System Updates
Regular Updates: Ensure all software and systems are regularly updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
Patch Management: Implement a robust patch management process to address security updates promptly.
10. Vendor and Third-Party Management
Vendor Security Assessments: Conduct regular security assessments of third-party vendors to ensure they comply with your security requirements.
Secure Integrations: Ensure any third-party services integrated with your systems meet stringent security standards.
11. Data Backup and Recovery
Regular Backups: Perform regular backups of critical data to secure locations.
Disaster Recovery Plan: Develop and maintain a disaster recovery plan to ensure quick recovery of data in case of a breach or loss.
12. Physical Security
Secure Access: Ensure physical access to servers and sensitive data storage areas is restricted to authorized personnel only.
Device Security: Secure all devices with strong passwords, encryption, and biometric authentication where possible.
Intranet on-premise or cloud? Which is safer?
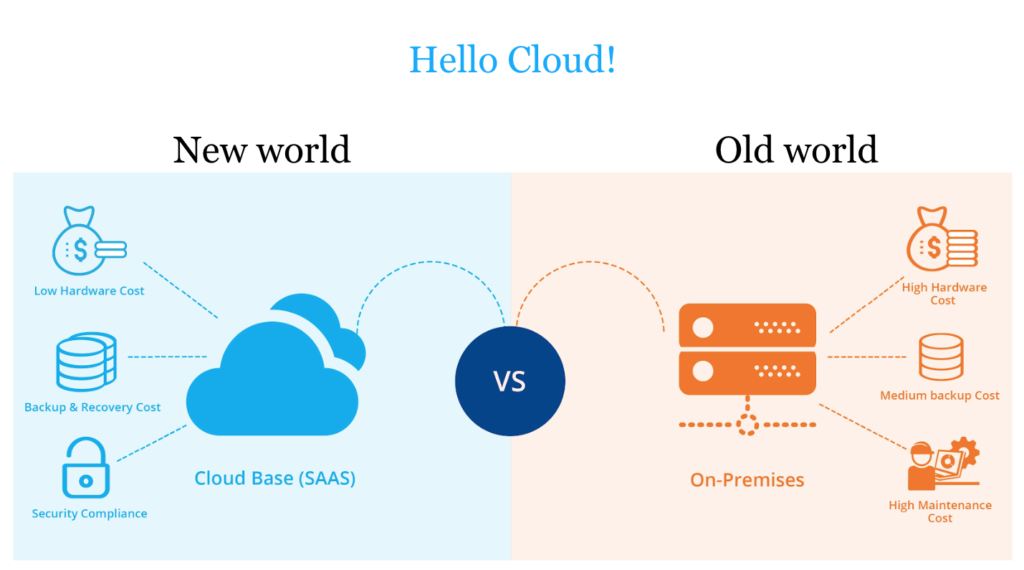
The security of an intranet, whether on-premises or cloud-based, depends on various factors, including implementation, management, and adherence to best practices. On-premises intranets offer direct control over the infrastructure, allowing organizations to tailor security measures to their specific needs and ensure physical security. However, this requires substantial resources for maintenance, regular updates, and comprehensive security protocols to protect against internal and external threats.
On the other hand, cloud-based intranets benefit from the advanced security measures provided by reputable cloud service providers, such as encryption, regular security updates, and compliance with global security standards. Cloud providers often have more resources to invest in cutting-edge security technologies and 24/7 monitoring. However, the security of a cloud-based intranet also depends on the organization’s ability to properly configure and manage cloud services, including access controls and data protection policies.
Ultimately, both on-premises and cloud-based intranets can be highly secure if managed correctly, but cloud-based solutions often offer superior scalability and advanced security features out-of-the-box, provided they are implemented and maintained with rigorous security practices.
Choose a secure internal communication platform with security certificates
Choosing an internal communication platform with security certificates is essential for ensuring robust data protection, compliance with international standards, and mitigating the risks associated with data breaches. Certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2 Type 2 indicate that a platform has undergone rigorous security assessments and adheres to best practices in information security management.
Staffbase exemplifies the standards of secure internal communication with its comprehensive security measures, including end-to-end encryption, regular security audits, and dedicated security and privacy teams. Opting for Staffbase ensures a secure, reliable, and compliant communication environment tailored to meet the highest security standards.









